Introduction to Project Management
Project management is the art and science of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals within defined constraints. It’s a crucial skill in today’s world, used in various industries to deliver projects on time, within budget, and to the required quality standards.
This introduction explores the importance of project management, the key components for success, and provides an overview of popular methodologies.
Understanding the Importance of Project Management
In today’s fast-paced environment, organizations rely on successful project completion to achieve strategic goals, launch new products, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. Here’s why project management is essential:
- Reduced Costs and Risks: Effective project management helps avoid costly mistakes and rework by planning, identifying potential issues early, and allocating resources efficiently.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Project management tools and techniques streamline workflows, optimize resource allocation, and ensure tasks are completed on time, leading to increased productivity.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Project management fosters clear communication between team members, stakeholders, and clients. This reduces misunderstandings and fosters collaboration for a successful outcome.
- Increased Stakeholder Satisfaction: By managing expectations, delivering projects on time and within budget, project management keeps stakeholders engaged and satisfied.
- Improved Innovation and Learning: Project management frameworks provide a structured approach to experimentation and learning from successes and failures. This fosters continuous improvement and innovation.
Examples of Projects Requiring Effective Management:
- Developing a new marketing campaign
- Launching a software application
- Constructing a new building
- Organizing a company event
- Implementing a new business process
Key Components of Successful Project Management
Effective project management relies on several key components:
- Project Scope Definition: Clearly define the project’s goals, deliverables, and boundaries. This ensures everyone understands what the project aims to achieve and avoids scope creep, which can lead to delays and budget overruns.
- Project Planning: Develop a detailed plan outlining tasks, timelines, dependencies, resources required, and a budget. This roadmap guides the project execution and helps anticipate potential challenges.
- Resource Management: Allocate the right people, equipment, and materials to complete project tasks effectively. This includes managing team schedules, skills, and workloads.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks that could impact the project, assess their likelihood and impact, and develop mitigation strategies to minimize their effect.
- Communication Management: Establish clear communication channels and protocols for regular updates with team members, stakeholders, and clients. This ensures everyone is informed and aligned with project progress.
- Change Management: Projects often encounter unforeseen changes. Effective project management involves adapting plans and processes to accommodate these changes while minimizing disruption.
- Quality Management: Implement quality control measures throughout the project lifecycle to ensure deliverables meet the required standards. This may involve reviews, testing, and inspections.
- Stakeholder Management: Identify and engage stakeholders who are impacted by the project. Manage their expectations, address their concerns, and keep them informed of progress.

Overview of Project Management Methodologies
Several project management methodologies offer different approaches to project execution. Choosing the right methodology depends on the project’s nature, size, and complexity. Here’s a brief overview of popular methods:
- Waterfall Methodology: This traditional approach follows a linear sequence of stages, with each stage completed before moving to the next. It’s suitable for well-defined projects with clear requirements.
- Agile Methodology: This iterative and flexible approach involves breaking down projects into smaller tasks (sprints) and continuously delivering and testing features. It’s ideal for projects with evolving requirements or a high degree of uncertainty.
- Scrum: A popular Agile framework that uses short sprints, daily stand-up meetings, and backlog prioritization to deliver projects in an iterative and incremental way.
- Kanban: Another Agile framework emphasizing continuous workflow with a visual board to track tasks. Tasks move through different stages (to-do, in progress, done) providing a clear view of progress.
- PRINCE2: A structured methodology often used in large-scale projects, emphasizing detailed planning, risk management, and change control procedures.
By understanding the importance of project management, its key components, and the available methodologies, individuals and organizations can significantly increase the chances of project success. Effective project management ensures projects are completed on time, within budget, and meet the desired quality standards, leading to greater efficiency, innovation, and achievement of organizational goals.
Planning Phase: Setting the Foundation
The planning phase is the cornerstone of any successful POS system implementation. It’s where you lay the groundwork, define your goals, and establish a clear roadmap for achieving them. This section dives into three crucial aspects of the planning phase:
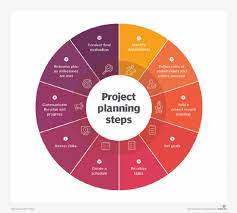
Defining Project Objectives and Scope
A well-defined project starts with clarity on what you want to achieve and what will be included (and excluded) from the project.
- Setting SMART Objectives:
Formulate clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for your POS system implementation. These objectives should directly address the needs of your business.
- Example: “Implement a cloud-based POS system within 3 months to streamline checkout processes, improve inventory management, and generate real-time sales reports that increase operational efficiency by 20%.”
- Understanding Stakeholder Needs:
Identify all stakeholders involved in the project, including managers, employees, customers, and the POS system vendor. Understanding their needs and expectations ensures a solution that benefits everyone.
- Defining Project Scope:
Clearly define the boundaries of the project. This includes the specific features and functionalities of the POS system to be implemented, the data to be migrated (if applicable), and any integrations with existing software.
Example Scope:
- The project will implement a cloud-based POS system with features for sales processing, inventory management, and basic customer relationship management (CRM).
- Data migration will be limited to historical sales data from the past year.
- Integration will occur with the existing accounting software.
Creating a Project Plan and Timeline
A comprehensive project plan keeps everyone on the same page and ensures timely implementation:
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS):
Break down the project into smaller, manageable tasks. This creates a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) that visualizes the project workflow and dependencies between tasks.
- Gantt Chart:
Develop a Gantt Chart to visualize the project timeline. This chart clarifies the duration of each task, their start and end dates, and any dependencies between them.
Consider key milestones such as:
- Contract signing with POS vendor
- Hardware and software installation
- Data migration completion
- Employee training sessions
- System go-live date
- Resource Allocation:
Assign specific tasks to team members based on their skills and expertise. This ensures everyone is aware of their responsibilities and deadlines.
Identifying Resources and Budget Allocation
A realistic budget and resource allocation are essential for successful implementation:
- Personnel:
Identify the personnel required for the project, including internal staff (IT department, managers, employees) and any external consultants. Estimate the time commitment needed from each team member.
- Hardware and Software:
Determine the hardware and software needs based on the chosen POS system and the size of your business. This may include POS terminals, barcode scanners, receipt printers, and any necessary software licenses.
- Training Costs:
Factor in the cost of employee training on the new POS system. This may involve in-person training sessions or online training modules provided by the POS vendor.
- Contingency Budget:
Allocate a contingency budget to address unforeseen costs that may arise during the implementation process.
Effective Communication:
Regularly communicate project updates, timelines, and any potential challenges to all stakeholders. This ensures everyone is informed and aligned with the project goals.
By meticulously defining your objectives, creating a comprehensive plan, and allocating resources effectively, you establish a solid foundation for a successful POS system implementation. This planning phase sets the stage for a smooth transition and maximizes the benefits your new system delivers.
Execution Phase: Bringing Plans to Life
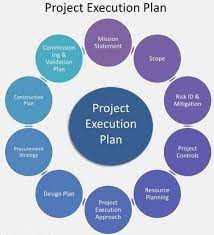
The planning phase has laid the groundwork, and now it’s time to translate those plans into action. The execution phase is where the real work of implementing your POS system takes place. This section explores three critical aspects of this crucial stage:
Assigning Tasks and Responsibilities
With a clear project plan in hand, it’s time to delegate tasks and establish ownership:
- Team Formation: Create a project team with representatives from various departments (IT, operations, sales) who will be responsible for specific aspects of the implementation.
- Task Delegation: Assign specific tasks within the WBS to team members based on their skills and expertise. Ensure each task has a clear owner who is accountable for its timely completion.
- RACI Matrix: Consider using a RACI Matrix to define roles and responsibilities. This matrix clarifies who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each task.
- Communication Plan: Establish a clear communication plan to ensure everyone is informed about project progress, task updates, and potential roadblocks. Regular team meetings and status reports are essential for maintaining transparency and fostering collaboration.
Monitoring Progress and Performance
Proactive monitoring is crucial for identifying and addressing any deviations from the plan:
- Milestones: Track progress against established milestones outlined in the project timeline. This allows for early identification of delays and enables corrective actions to be taken.
- Performance Indicators: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure project progress. These may include task completion rates, employee training completion, and system testing results. Regularly monitor these KPIs to assess if the project is on track.
- Tracking Tools: Utilize project management tools or spreadsheets to track tasks, dependencies, and deadlines. These tools provide a centralized platform for monitoring progress and ensuring everyone has access to the latest information.
- Reporting: Develop regular reports that communicate project progress, identify potential risks, and highlight areas requiring adjustments. Share these reports with stakeholders to maintain transparency and ensure alignment.
Addressing Issues and Risks in Real-Time
Even the most meticulous plans can encounter unforeseen challenges. The key is to have a proactive approach to addressing issues and mitigating risks:
- Risk Management Plan: Refer back to the risk management plan developed during the planning phase. This plan should have identified potential risks and outlined mitigation strategies.
- Problem-solving: Assemble the project team to brainstorm solutions for any issues that arise. Encourage open communication and collaboration to find effective solutions.
- Proactive Communication: Communicate any roadblocks or delays to stakeholders promptly. Transparency fosters trust and allows stakeholders to adjust expectations if necessary.
- Change Management: Be prepared to adapt the project plan as needed. If unforeseen circumstances necessitate adjustments, clearly communicate the changes to all stakeholders and update the project documentation accordingly.
Maintaining Focus:
The execution phase requires focus and discipline. By effectively delegating tasks, monitoring progress, and proactively addressing challenges, you can ensure the project stays on track and delivers the desired outcomes. Regularly evaluate the project’s health and make adjustments as needed to keep your POS system implementation moving smoothly towards a successful completion.
Monitoring and Control: Ensuring Project Success
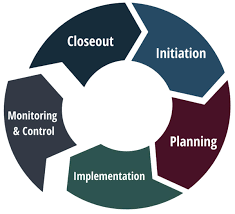
The execution phase is in full swing, and now it’s critical to maintain close oversight to guarantee a successful POS system implementation. This section delves into three crucial aspects of the monitoring and control phase:
Tracking Milestones and Deliverables
Continuous monitoring of progress against established benchmarks ensures timely completion and adherence to the project plan:
- Milestone Tracking: Regularly track progress towards established milestones outlined in the project timeline. These milestones represent key stages in the implementation process, such as hardware installation, data migration completion, or employee training sessions.
- Performance Indicators: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) defined earlier. These may include task completion rates, test results, and employee training progress. Deviations from expected performance levels indicate potential issues requiring attention.
- Progress Reports: Generate regular progress reports that detail completed tasks, upcoming deadlines, and any encountered challenges. Share these reports with stakeholders to maintain transparency and foster collaboration.
- Corrective Actions: If progress reports or KPI monitoring reveal deviations from the plan, take corrective actions promptly. This might involve adjusting resource allocation, modifying timelines, or implementing alternative solutions to get the project back on track.
Implementing Change Management Processes
The business environment is rarely static, and unforeseen circumstances may necessitate adjustments to the project plan. A robust change management process helps navigate these situations effectively:
- Adaptability: Embrace a flexible approach that allows for adjustments to the plan as needed. Be prepared to adapt to new information, address emerging issues, or incorporate valuable stakeholder feedback.
- Stakeholder Communication: Proactively communicate any changes to the project plan to all stakeholders. Clearly explain the rationale behind the changes and address any concerns they may have. Transparency builds trust and ensures everyone remains aligned with the project goals.
- User Adoption: A successful POS system implementation hinges on user adoption by employees. Involve employees throughout the process, address their concerns, and provide adequate training to ensure they feel comfortable and confident using the new system.
Adjusting Plans as Needed to Stay on Track
The ability to adapt the project plan as needed is crucial for navigating unforeseen challenges and ensuring project success:
- Risk Management: Continuously monitor potential risks identified during the planning phase. Proactively address any emerging risks and implement the mitigation strategies outlined in the risk management plan.
- Reprioritization: If circumstances necessitate, prioritize tasks to ensure critical activities are completed on time. Communicate these adjustments to stakeholders and explain the rationale behind the revised plan.
- Resource Allocation: Dynamically allocate resources based on project needs. If certain tasks require additional attention, shift resources accordingly to maintain project momentum.
Importance of Documentation:
Maintain comprehensive project documentation throughout the monitoring and control phase. This includes meeting minutes, progress reports, change logs, and issue resolution records. This documentation serves as a valuable historical record and ensures a smooth handover if personnel changes occur during the implementation process.
Conclusion:
By closely monitoring progress, implementing effective change management processes, and adapting plans as needed, you can ensure your POS system implementation stays on track and delivers the desired outcomes. Remember, clear communication, adaptability, and a focus on user adoption are paramount for achieving successful project completion. The well-implemented POS system will then serve as a powerful tool to streamline operations, empower data-driven decision making, and elevate the customer experience within your business.
Communication and Collaboration: Key to Team Success

A successful POS system implementation hinges not only on meticulous planning and execution but also on fostering a collaborative and communicative work environment. This section highlights the importance of effective communication and collaboration for a well-functioning project team.
Establishing Effective Communication Channels
Open communication is the cornerstone of successful teamwork. Here are ways to establish effective communication channels:
- Defined Communication Channels: Establish clear communication channels for different purposes. Utilize a project management tool for task updates, email for detailed discussions, and instant messaging platforms for quick questions or clarifications.
- Regular Meetings: Schedule regular project team meetings to discuss progress, address challenges, and brainstorm solutions. Encourage open communication and active participation from all team members.
- Transparency: Maintain transparency throughout the project. Share project updates, roadblocks, and decision-making processes with all stakeholders. This fosters trust and ensures everyone is aligned with the project goals.
- Accessibility: Ensure key decision-makers and project leads are easily reachable for questions or clarifications. This minimizes delays and fosters a sense of ownership among team members.
Promoting Collaboration and Teamwork
A strong team spirit is vital for successful project completion. Here’s how to promote collaboration and teamwork:
- Shared Goals: Clearly communicate the project goals and objectives to all team members. This fosters a sense of shared purpose and motivates everyone to contribute their best efforts.
- Team Building Activities: Consider incorporating team-building activities to enhance communication, collaboration, and problem-solving skills within the team.
- Recognition and Appreciation: Recognize and appreciate individual and team achievements. This reinforces positive behaviors, motivates team members, and strengthens team morale.
- Knowledge Sharing: Encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration between team members with different skill sets. This fosters a learning environment and leverages the diverse expertise within the team.
Resolving Conflicts and Enhancing Team Dynamics
Even the most collaborative teams can experience disagreements. Here’s how to navigate conflicts constructively:
- Conflict Resolution Skills: Equip team members with basic conflict resolution skills. Encourage active listening, respectful communication, and a focus on finding solutions rather than assigning blame.
- Active Listening: Practice active listening during discussions. Pay attention to concerns, acknowledge different perspectives, and strive to find common ground.
- Respectful Communication: Maintain a respectful and professional tone throughout communication, even during disagreements. Focus on the issue at hand, avoid personal attacks, and prioritize finding solutions that benefit the project.
- Team Dynamics Assessment: Regularly assess team dynamics. Identify areas for improvement and address any underlying issues that may be hindering collaboration.
By fostering open communication, promoting collaboration, and constructively resolving conflicts, you create a positive and productive work environment. This, in turn, fuels project success and ensures a smooth POS system implementation.
Project Closure: Evaluating Success and Lessons Learned

The POS system implementation journey nears its completion. The final phase focuses on evaluating success, capturing valuable insights, and acknowledging the team’s efforts.
Conducting Project Reviews and Evaluations
- Assess how well the project met its initial objectives outlined in the planning phase.
- Evaluate project performance against established KPIs such as budget adherence and timeline milestones.
- Gather feedback from stakeholders and team members on the implementation process.
Documenting Lessons Learned and Best Practices
- Capture key learnings and best practices encountered throughout the project.
- Document challenges faced and solutions implemented for future reference.
- This knowledge base serves as a valuable resource for future POS system implementations within your organization.
Celebrating Achievements and Recognizing Team Contributions
- Acknowledge the team’s hard work and dedication throughout the project.
- Celebrate the successful implementation of the new POS system.
- Recognizing individual and team contributions fosters a sense of accomplishment and motivates future endeavors.
Successfully implementing a new POS system requires meticulous planning, effective execution, and a commitment to clear communication and collaboration. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge and tools to navigate each stage of the process, from defining project objectives to evaluating success. By following these steps and adapting them to your specific business needs, you can ensure a smooth POS system implementation that empowers your business for long-term success. The new system will streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and provide valuable data to fuel informed decision-making, propelling your business towards a prosperous future.
Future Trends in Project Management: A Glimpse Ahead
The project management landscape is constantly evolving. Here’s a peek into some key trends shaping the future:
Embracing Agile and Lean Methodologies:
- Traditional, rigid project management approaches are giving way to agile and lean methodologies.
- Agile focuses on iterative development and continuous improvement, while lean prioritizes eliminating waste and maximizing value.
These approaches enable faster adaptation to change and increased project flexibility.
Harnessing the Power of Automation and AI:
- Automation is streamlining repetitive tasks, freeing up project managers to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Artificial intelligence (AI) is assisting with project planning, risk assessment, and resource allocation.
- These technologies are enhancing efficiency, improving decision-making, and reducing human error.
Adapting to Remote Work and Distributed Teams:
- The rise of remote work necessitates robust collaboration tools and effective communication strategies.
- Project managers need to adapt their leadership styles to manage geographically dispersed teams.
- Building trust, fostering virtual team dynamics, and leveraging technology will be crucial for success.
By embracing these trends, project managers can stay ahead of the curve and ensure their teams deliver exceptional results in the ever-changing business environment.
Project Management Tools and Technologies: Optimizing Your Workflow

Equipping yourself with the right tools can significantly enhance project management efficiency. This section explores some valuable technologies to consider:
Introduction to Project Management Software
- Project management software offers a centralized platform for task management, resource allocation, communication, and progress tracking.
- Popular options include Asana, Trello, and Monday.com, each catering to different needs and preferences.
Utilizing Collaboration Platforms and Tools
- Effective communication is vital for project success.
- Collaboration platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams facilitate real-time communication, file sharing, and video conferencing, fostering seamless collaboration even with remote teams.
Integrating Project Management with Other Business Systems
- Integrate your project management software with other business systems you use, such as accounting software or CRM systems.
- This eliminates data silos, streamlines workflows, and ensures everyone has access to the latest information.
By leveraging these project management tools and technologies, you can optimize your workflow, enhance team collaboration, and ensure your projects run smoothly and efficiently.
Project Management Best Practices and Tips: Your Toolkit for Success
Even the most sophisticated tools won’t guarantee project success. Here are some core best practices to keep in mind:
Setting Clear and Achievable Goals
- Clearly define SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) for each project.
- Well-defined goals provide direction, focus efforts, and serve as benchmarks for measuring success.
Prioritizing Tasks and Managing Time Effectively
- Prioritize tasks based on importance and urgency. Utilize techniques like the Eisenhower Matrix to categorize tasks and allocate time efficiently.
- Effective time management skills ensure critical tasks are completed on time and project deadlines are met.
Empowering Teams and Encouraging Innovation
- Foster a collaborative environment where team members feel empowered to contribute their ideas and expertise.
- Encourage open communication and celebrate innovation. This fosters a sense of ownership and motivates teams to deliver their best work.
By implementing these best practices and leveraging the right tools, you can effectively manage projects, empower your team, and achieve exceptional results.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Project Management
Successfully implementing a POS system, or any project for that matter, requires a blend of strategic planning, meticulous execution, and a commitment to clear communication and collaboration. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge and tools to navigate each stage of the project management journey, from defining objectives and establishing a roadmap to evaluating success and learning from the experience.
Remember, project management is an ongoing process of learning and adaptation. By embracing new trends like agile methodologies and leveraging powerful technologies like automation and AI, you can stay ahead of the curve and ensure your projects deliver exceptional results.
Ultimately, mastering the art of project management empowers you to transform ideas into reality, optimize workflows, and drive your business towards long-term success. So, equip yourself with the best practices, utilize the right tools, and foster a collaborative environment – and watch your projects flourish!