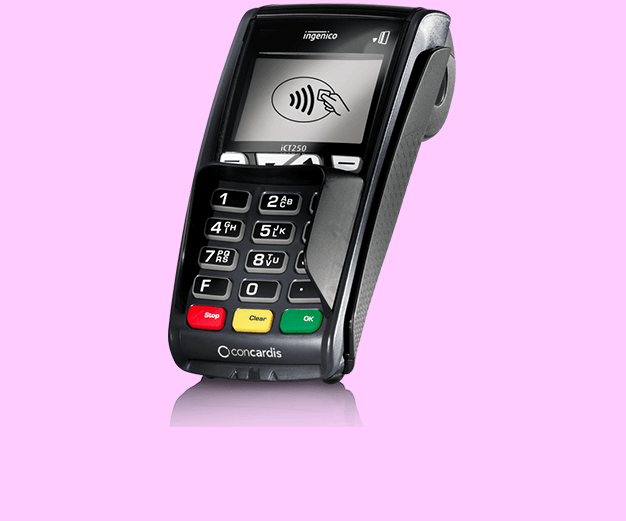
Introduction to Point of Sale (POS) Systems: The Engine of Retail Transactions
In today’s dynamic retail landscape, a seamless and efficient checkout experience is crucial for customer satisfaction and business success. Enter Point of Sale (POS) systems – the technological backbone of modern transactions. This section delves into the history and evolution of POS systems, explores their vital role in business operations, and unpacks the key components that make them work.
Definition and Evolution of POS Systems

A POS system is the technological hub at the heart of a retail transaction. It’s the software and hardware combination that allows businesses to:
- Record sales: Capture product details, quantities, and prices.
- Process payments: Accept cash, credit cards, debit cards, and other payment methods.
- Manage inventory: Track stock levels and generate reports for reordering.
- Print receipts: Provide customers with a record of their purchase.
- The Evolution of POS Systems:
- Early Cash Registers (1879): James Ritty invented the first mechanical cash register to track sales and deter employee theft.
- Electronic Cash Registers (1960s): These replaced mechanical models, offering faster transaction processing and basic sales data recording.
- PC-based POS Systems (1980s): Personal computers revolutionized POS systems, enabling more sophisticated features like inventory management and customer tracking.
- Touchscreen POS Systems (1990s): User-friendly touchscreen interfaces simplified operations and improved transaction speed.
- Cloud-based POS Systems (Present Day): The rise of cloud technology allows for remote access, data storage, and system updates, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
Importance of POS in Business Operations

POS systems are no longer just cash registers; they are essential tools for effective business management:
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined transactions, faster checkout times, and automated processes lead to improved operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Sales Management: POS systems provide valuable sales data for analysis, allowing businesses to track sales trends, identify best-selling products, and optimize pricing strategies.
- Improved Inventory Management: Real-time inventory tracking helps businesses prevent stockouts, minimize overstocking, and optimize ordering processes.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Faster checkouts, efficient payment processing, and the ability to offer loyalty programs contribute to a positive customer experience.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: POS systems generate valuable data that empowers businesses to make informed decisions about product selection, marketing strategies, and staffing levels.
Key Components of a POS System
A comprehensive POS system typically comprises three key elements:
- Hardware:
- POS Terminal: The central unit, often a computer or tablet, running the POS software and facilitating interaction with other hardware components.
- Barcode Scanner: Reads product barcodes for quick and accurate product identification.
- Receipt Printer: Prints customer receipts for purchases.
- Cash Drawer: Securely stores cash payments.
- Customer Display: Shows the customer the transaction details and purchase amount.
- Software:
- POS Software: The heart of the system, handling all transaction processing, data management, and communication with hardware components. Features may include inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and sales reporting.
- Security Software: Protects sensitive customer data and financial information.
- Peripheral Devices:
- Payment Card Reader: Processes credit card and debit card payments.
- Pole Display: Displays transaction details and promotions for customers at the checkout area.
- Weight Scale: Used for products sold by weight.
Choosing the Right POS System:
The ideal POS system for a business depends on factors like industry, transaction volume, and budget. Options range from basic cloud-based systems for small businesses to feature-rich solutions for larger retail chains.
By understanding the evolution, importance, and components of POS systems, businesses can make informed decisions about integrating this essential technology into their operations, paving the way for a more efficient, data-driven, and customer-centric approach to retail success.
Types of POS Systems and Their Applications

With the understanding of the core functionalities of POS systems, we can delve deeper into the various types available and how they cater to specific business needs. This section explores traditional vs. cloud-based solutions, industry-specific POS applications, and the growing significance of mobile POS systems.
Traditional vs. Cloud-Based POS Systems
The two main categories of POS systems are differentiated by software deployment:
- Traditional (On-Premises) POS Systems:
Features:
Installed on a local server within the business, offering full control over data and software.
Benefits:
- Customization: Businesses can customize the software to meet their specific needs.
- Security: Data resides on-site, potentially offering a higher level of perceived security (although proper security measures are crucial for both systems).
Drawbacks:
- High Upfront Cost: Requires investment in hardware, software licenses, and IT infrastructure.
- Limited Scalability: Expanding the system can be complex and expensive.
- Maintenance: Businesses are responsible for software updates, security patches, and hardware maintenance.
- Cloud-Based POS Systems:
Features:
Software resides on remote servers accessed through an internet connection.
Benefits:
- Affordability: Subscription-based model often requires lower upfront costs.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate business growth.
- Automatic Updates: Software updates and security patches are handled by the provider.
- Remote Access: Access the system from any internet-connected device.
Drawbacks:
- Internet Dependence: Requires a reliable internet connection for functionality.
- Data Security Concerns: Businesses must trust the cloud provider’s security measures.
Choosing Between Traditional and Cloud-Based Systems:
The ideal choice depends on factors like budget, technical expertise, and internet connectivity:
- Traditional systems may be suitable for businesses with specific customization needs, high security concerns, and reliable on-site IT infrastructure.
- Cloud-based systems offer greater affordability, scalability, and ease of use, making them popular for a wide range of businesses, especially those with limited IT resources.
Industry-Specific POS Applications
POS systems can be customized to cater to the specific needs of different industries:
- Retail POS Systems: Manage product sales, inventory, customer loyalty programs, and age verification (for age-restricted products). May integrate with barcode scanners and label printers.
- Hospitality POS Systems: Handle restaurant and bar orders, table management, kitchen display systems, and split bills. May integrate with kitchen printers and online ordering platforms.
- Healthcare POS Systems: Manage patient check-in, appointment scheduling, insurance verification, and billing. May integrate with electronic health records (EHR) systems and appointment scheduling software.
These industry-specific systems often have additional features tailored to the unique workflows and regulations of each sector.
Mobile POS and Its Growing Significance
Mobile POS (mPOS) systems leverage tablets or smartphones equipped with POS software to process transactions:
Features:
Allow for transactions anywhere within a business or even outside a physical location (e.g., farmers markets, pop-up shops).
Benefits:
- Increased Flexibility: Enable transactions outside traditional checkout areas.
- Reduced Costs: Lower investment compared to traditional POS systems.
- Improved Customer Service: Process transactions at the customer’s location (e.g., tableside in a restaurant).
Drawbacks:
- Limited Functionality: May not offer all the features of a traditional POS system.
- Security Concerns: Mobile devices require robust security measures to protect sensitive data.
The Rise of mPOS:
The growing popularity of mobile payments and the demand for greater flexibility are driving the adoption of mPOS solutions across various industries. Restaurants can utilize mPOS for tableside ordering, retailers can manage sales at pop-up events, and service providers can accept payments on-site.
By understanding the different types of POS systems and their industry-specific applications, businesses can select the solution that best fits their operational needs, budget, and future growth plans. As mobile technology continues to evolve, mPOS is likely to play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of retail and beyond.
Choosing the Right POS System for Your Business: A Guide to Success
Selecting the right POS system is a crucial decision for businesses of all sizes. A well-chosen system can streamline operations, boost efficiency, and enhance customer experience. However, navigating the vast array of POS options can be overwhelming. This section empowers you with the knowledge required to make an informed decision, guiding you through assessing your business needs, identifying essential features, and ensuring seamless integration with existing tools.
Assessing Business Needs and Requirements
Before diving into specific features, it’s essential to take a step back and evaluate your unique business needs. Here are key considerations:
- Industry: Different industries have specific requirements. Retail POS systems need robust inventory management, while restaurant POS systems should prioritize order management and kitchen displays.
- Business Size and Growth Potential: Choose a system that can scale with your business. Cloud-based solutions often offer greater scalability compared to traditional systems.
- Budget: POS system costs vary depending on features, deployment model (cloud-based vs. traditional), and additional hardware needs. Determine your budget upfront to avoid exceeding your financial limitations.
- Technical Expertise: Consider your IT capabilities. Cloud-based systems typically require less in-house IT expertise compared to traditional systems.
- Desired Features: Make a list of functionalities important to your business, such as inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), reporting tools, or mobile POS capabilities.
Features to Look for in a POS System
Once you have a clear understanding of your business needs, delve into essential POS system features:
- Inventory Management: Effective tracking of stock levels, including low-stock alerts and purchase order generation, is crucial to avoid stockouts and optimize ordering.
- Sales Reporting: Detailed sales reports provide valuable insights into sales trends, product performance, and customer behavior. This data can inform marketing strategies, product selection, and staffing decisions.
- Customer Management: Features like customer loyalty programs, purchase history tracking, and contact information management can enhance customer relationships and encourage repeat business.
- Payment Processing: Securely process various payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, contactless payments, and mobile wallets.
- Employee Management: Manage employee profiles, track work hours, and set permissions for different user roles.
- Security: Data security is paramount. Look for systems that employ encryption, secure login protocols, and regular security updates to protect sensitive customer and financial information.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface with intuitive features is essential for efficient operation and minimal training time for employees.
Prioritizing Features:
Not all features will be equally important to your business. Prioritize those that directly address your operational needs and contribute to your business goals.
Integration with Other Business Tools
For optimal efficiency, your POS system should seamlessly integrate with your existing business tools:
- Accounting Software: Automatic integration with accounting software eliminates manual data entry and ensures accurate financial records.
- Inventory Management Software: Streamline inventory management by integrating your POS with dedicated inventory management software, especially for businesses with complex inventory needs.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Integrate your POS system with your CRM to gain a holistic view of customer interactions and personalize marketing efforts.
- Ecommerce Platform (if applicable): Ensure a seamless omnichannel experience by integrating your POS system with your online store, allowing for real-time inventory updates and synchronized customer data.
Leveraging APIs:
Many POS systems offer open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for integration with third-party applications. This expands the functionality of your POS system and caters to your specific business needs.
Choosing the Right Partner:
Selecting a POS system provider goes beyond just the software. Consider the quality of customer support, training resources offered, and the provider’s track record in your industry.
By diligently assessing your business needs, prioritizing essential features, and ensuring seamless integration with existing tools, you can confidently select the right POS system that empowers your business for long-term success. This investment will streamline operations, enhance customer experience, and equip you with valuable data to make informed business decisions, propelling your business towards a prosperous future.
Implementing and Optimizing Your POS System: Powering Efficiency and Growth
Selecting the right POS system is just the first step. Successful implementation and ongoing optimization are crucial for maximizing the benefits of your investment. This section guides you through the installation and setup process, highlights best practices for security, and emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and optimization.
Installation and Setup Process
A smooth implementation process ensures your POS system is operational quickly and efficiently:
- Onboarding: Most POS providers offer comprehensive onboarding support. This may include data migration from your previous system, hardware installation, and software configuration.
- System Configuration: Work with the provider to configure the system according to your specific business needs. This includes setting up tax rates, product categories, user accounts, and payment processing options.
- Employee Training: Invest in thorough training for your employees to ensure they are comfortable using the new system and can leverage its full potential. A user-friendly interface with intuitive features minimizes training time.
- Testing: Before going live, thoroughly test all functionalities of the POS system, including payment processing, inventory management, and reporting tools.
Best Practices for POS System Security
Since your POS system handles sensitive customer and financial information, robust security measures are essential:
- Data Encryption: Ensure the POS system encrypts data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access in case of a breach.
- Strong Passwords: Enforce strong password policies for user accounts, and require regular password changes.
- User Authentication: Implement a multi-factor authentication process for added security, especially for users with administrative privileges.
- Regular Updates: Keep your POS software and hardware up-to-date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities discovered by vendors.
- Physical Security: Secure your POS hardware in a restricted area and implement access controls to prevent unauthorized use.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Educate your employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and avoiding suspicious links or attachments.
By implementing these security measures, you can minimize the risk of data breaches and protect your business from financial losses and reputational damage.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization
Your POS system should be a living tool, continuously monitored and optimized for maximum efficiency:
- Data Analytics: Leverage built-in analytics tools to gain insights into sales trends, inventory levels, and customer behavior. Use this data to identify areas for improvement, such as optimizing product placement, adjusting pricing strategies, and managing staff scheduling.
- Performance Tracking: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as transaction processing speed, checkout times, and system uptime. Identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to optimize system performance.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews of your POS system to assess if it continues to meet your evolving business needs. New features or integrations may become necessary as your business grows.
- System Upgrades: Take advantage of software updates and upgrades offered by your POS provider. These may include new features, improved functionality, and enhanced security measures.
Investing in Ongoing Optimization:
By continuously monitoring and optimizing your POS system, you can ensure it remains a valuable tool that supports your business growth. Utilize the data and insights it provides to make informed decisions, streamline operations, and enhance the customer experience.
A well-chosen, implemented, and optimized POS system is a powerful asset for any business. It streamlines transactions, empowers data-driven decision making, and enhances customer service. By following the guidance provided in this comprehensive guide, you can navigate the POS selection process with confidence, implement your system effectively, and unlock its full potential to propel your business towards long-term success.
Overcoming Challenges and Troubleshooting: Keeping Your POS Running Smoothly
Even with a well-chosen and implemented POS system, occasional challenges can arise. This section equips you with the knowledge to address common issues and troubleshoot effectively, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operations.
Common Issues in POS Systems
While POS systems are designed for reliability, some common issues can occur:
- Connectivity Problems: Internet connectivity issues can disrupt transactions and cloud-based POS functionality.
- Software Glitches: Software bugs or errors may lead to inaccurate data, system crashes, or unexpected behavior.
- Hardware Failures: Hardware components like printers, barcode scanners, or the POS terminal itself can malfunction.
- User Errors: Accidental mistakes during data entry or improper system usage can cause discrepancies.
Troubleshooting Tips and Solutions
Here are some practical tips for troubleshooting common POS system issues:
- Restart the System: A simple system restart can often resolve software glitches and temporary malfunctions.
- Check Network Connectivity: Ensure a stable internet connection for cloud-based systems. Troubleshoot any network connectivity issues with your internet service provider.
- Consult User Guides and FAQs: Most POS providers offer comprehensive user guides and FAQs that address common troubleshooting steps.
- Contact Technical Support: Don’t hesitate to contact your POS provider’s technical support team for assistance with more complex issues. They can remotely diagnose the problem and provide guidance or solutions.
- Maintain Backups: Regularly back up your POS data to minimize potential data loss in case of hardware failure or software errors.
Developing a Proactive Approach:
- Regular System Updates: Ensure your POS software and hardware are updated with the latest patches to address vulnerabilities and bugs.
- Invest in preventative maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance for your POS hardware to identify and address potential issues before they cause downtime.
- Employee Training: Proper training on the POS system minimizes user errors and empowers employees to handle basic troubleshooting steps.
By familiarizing yourself with common issues and proactive measures, you can effectively troubleshoot challenges and minimize downtime. Additionally, having a reliable technical support team readily available ensures a swift resolution to more complex problems. Remember, a well-maintained POS system is essential for a smooth-running and successful business.
Future Trends in POS Technology: A Glimpse into Tomorrow’s Retail
The POS landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-changing needs of businesses and consumers. This section explores some of the exciting trends that will shape the future of POS technology:
Advancements in Payment Technologies
The way we pay is undergoing a significant transformation, and POS systems are at the forefront of these changes:
- Frictionless Payments: Contactless payments using mobile wallets and NFC technology are becoming increasingly popular. POS systems will seamlessly integrate with these methods for a faster and more convenient checkout experience.
- Cryptocurrency Integration: As cryptocurrency adoption grows, POS systems may offer the ability to accept crypto payments, catering to a tech-savvy customer base.
- Biometric Authentication: Biometric technologies like fingerprint or facial recognition scanners could be integrated into POS systems for secure and convenient customer identification and payment authorization.
Enhanced Customer Engagement through POS
POS systems are no longer just transactional tools; they are powerful tools for building stronger customer relationships:
- Personalized Customer Experiences: POS systems can leverage customer data to offer personalized promotions, targeted recommendations, and loyalty program rewards, fostering customer engagement and brand loyalty.
- Omnichannel Integration: Seamless integration with online stores allows for a unified customer experience across all touchpoints, whether shopping online or in-store.
- Real-time Customer Insights: POS data can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, buying patterns, and preferences. Businesses can leverage this data to refine marketing strategies, optimize product offerings, and personalize customer interactions.
The Future of POS: A Collaborative Ecosystem
These trends point towards a future where POS systems become intelligent hubs within a collaborative ecosystem. They will not only handle transactions but also provide valuable data for informed decision-making, facilitate personalized customer experiences, and adapt to the ever-evolving retail landscape.
Case Studies: POS Systems Powering Business Success
Witnessing how other businesses leverage POS systems for success can be highly valuable. This section can be a placeholder where you can include 2-3 brief case studies highlighting real-world examples:
- Case Study 1: Streamlined Operations and Increased Sales for a Boutique Clothing
Store: A boutique implements a cloud-based POS system with inventory management features. This reduces stockouts, optimizes ordering, and improves overall operational efficiency. The system also integrates with a loyalty program, leading to a significant increase in repeat business.
- Case Study 2: Enhanced Customer Experience Boosts Revenue for a Coffee Shop
Chain: A coffee shop chain integrates mobile POS tablets, enabling faster table-side ordering and payment processing. This streamlines customer service and reduces wait times, leading to increased customer satisfaction and revenue growth.
Focus on ROI and Business Growth:
By showcasing real success stories, emphasize the positive impact POS systems can have on businesses, including improved operational efficiency, increased sales, and enhanced customer experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a well-implemented Point of Sale (POS) system stands as a cornerstone for businesses aiming to maximize efficiency and profitability. By seamlessly integrating technology into the transactional process, businesses can streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and gain valuable insights into their operations.
The comprehensive nature of a POS system, from traditional setups to modern cloud-based solutions, empowers businesses across various industries. As businesses transition towards mobile and flexible POS options, they unlock newfound agility and adaptability in their operations.
Selecting the right POS system involves a careful consideration of business needs, features, and integration capabilities. The ongoing commitment to security, continuous monitoring, and optimization ensures the sustained effectiveness of the POS system.
Despite potential challenges, businesses can overcome them by implementing best practices, leveraging technical support, and staying informed about troubleshooting solutions. The future trends in POS technology, such as contactless payments, cryptocurrency integration, and enhanced customer engagement, promise to shape the landscape of retail and service industries.
Real-world case studies further emphasize the transformative impact of POS systems on businesses, showcasing tangible success stories, return on investment, and overall business growth.
In essence, by embracing the evolving landscape of POS technology, businesses can harness the power of efficient transactions, data-driven decision-making, and enhanced customer relationships. The journey towards maximizing efficiency and profitability with POS systems is not just an investment in technology; it’s an investment in the future success of the business.